Gastric bypass is one of the most trusted and effective weight loss surgeries performed worldwide. Many people struggling with obesity and related health problems often ask a simple but important question: how does gastric bypass work?
This surgery does more than just reduce food intake—it changes how your body processes food, controls hunger, and manages blood sugar levels.
In this detailed guide, we will explain how gastric bypass works step by step, who it is suitable for, how it helps in weight loss and disease control, what changes you can expect after surgery, and common questions patients usually have.
Understanding Gastric Bypass Surgery
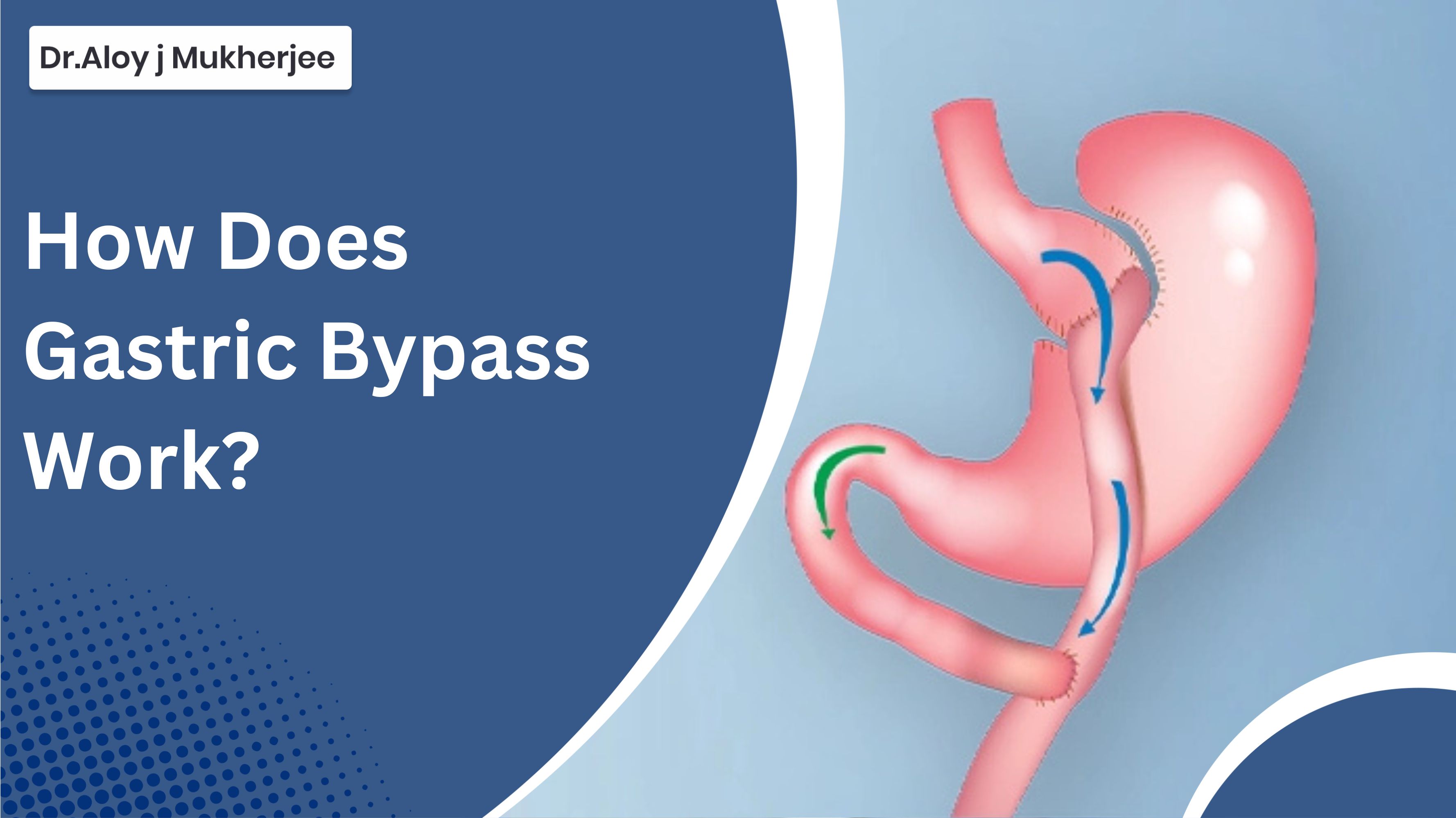
Gastric bypass, medically known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is a weight loss procedure that helps people lose excess weight by changing the structure of the stomach and small intestine.
Unlike dieting alone, this surgery works on three levels:
Reduces the amount of food you can eat
Changes how nutrients are absorbed
Alters hunger and fullness hormones
Because of these combined effects, Gastric Bypass Surgery in Delhi is often recommended for people who have not achieved long-term weight loss through diet, exercise, or medications.
How Does Gastric Bypass Work?
To truly understand how does gastric bypass work, think of it as a rewiring of your digestive system.
The surgery works in two main ways:
Restriction – limits how much you can eat
Malabsorption – reduces how many calories your body absorbs
Together, these changes help the body lose weight safely and effectively.
Step-by-Step: How Gastric Bypass Surgery Is Performed
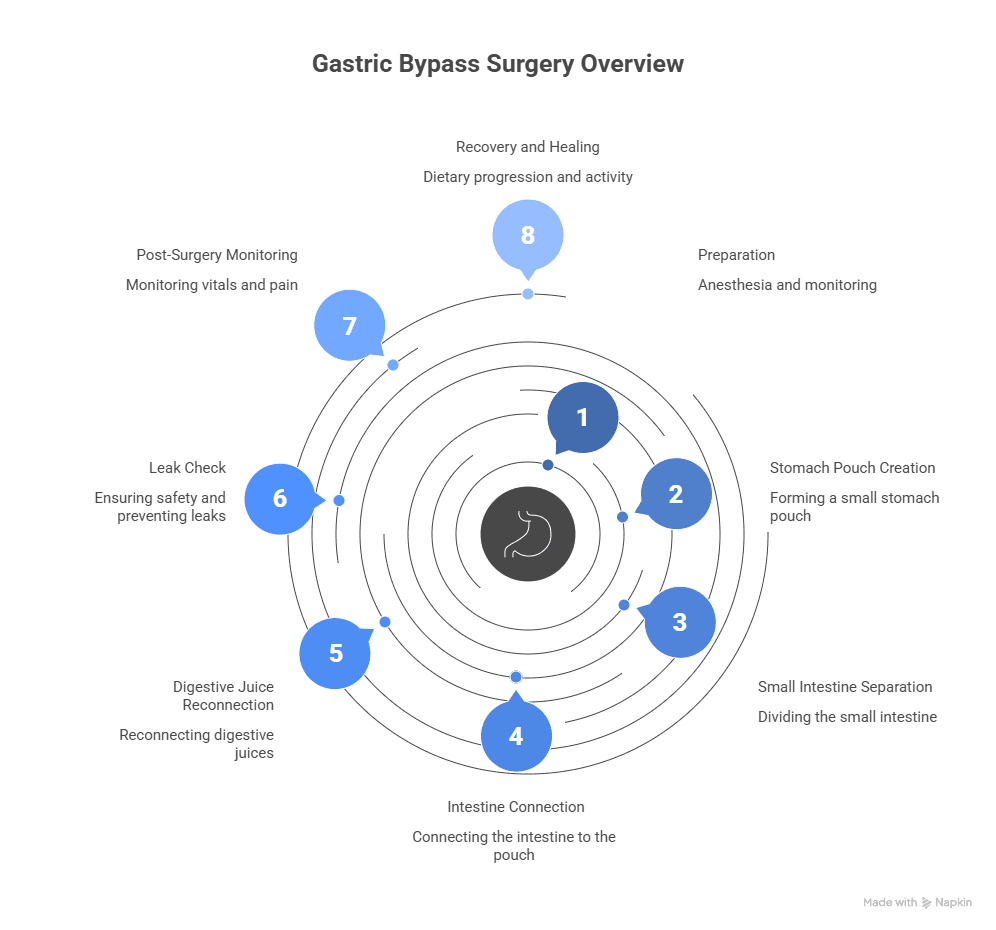
1. Preparation Before Surgery
Before gastric bypass surgery begins, the patient is prepared under strict medical protocols. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, which means the patient is completely asleep and feels no pain. Vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels are continuously monitored throughout the surgery to ensure safety.
Patient is given general anesthesia
Surgery is usually done using a minimally invasive (laparoscopic) technique
Small incisions are made in the abdomen
Specialized surgical instruments and a camera are used
2. Creation of a Small Stomach Pouch
In this step, the surgeon divides the upper part of the stomach to create a very small pouch. This pouch becomes the new stomach and can hold only a small amount of food. The rest of the stomach remains inside the body but no longer receives food directly.
New stomach pouch is about the size of a lemon
Original stomach is not removed, only bypassed
Patient feels full after eating a small quantity
Helps control portion size naturally
3. Separation of the Small Intestine
After creating the stomach pouch, the surgeon identifies and divides a portion of the small intestine. This step is essential because it allows food to bypass part of the digestive system, reducing calorie absorption.
Small intestine is carefully divided
Upper portion remains connected to digestive juices
Lower portion will carry food from the new stomach pouch
This step prepares the intestine for rerouting
4. Connecting the Intestine to the New Stomach Pouch
The lower part of the small intestine is then directly connected to the new stomach pouch. This allows food to move straight from the pouch into the intestine, skipping most of the stomach and the first part of the intestine.
Food bypasses a large portion of the digestive tract
Fewer calories and nutrients are absorbed
Helps in faster and sustained weight loss
Reduces spikes in blood sugar levels
5. Reconnecting Digestive Juices to the Intestine
To ensure proper digestion, the upper part of the small intestine (which carries bile and digestive enzymes) is reconnected further down. This allows digestive juices to mix with food at a later stage.
Digestive enzymes still work normally
Nutrient absorption is controlled, not completely stopped
Helps maintain digestion while limiting calorie intake
Prevents severe digestive problems
6. Checking for Leaks and Safety
Once all connections are completed, the surgeon carefully checks for leaks or weak points. This step is critical to avoid complications after surgery. The surgical area is then cleaned, and incisions are closed.
Leak tests are performed
Blood flow and connections are rechecked
Incisions are closed with sutures or staples
Surgery usually takes 2–3 hours
7. Immediate Post-Surgery Monitoring
After surgery, the patient is moved to a recovery area for close monitoring. Pain control, hydration, and breathing are carefully managed. Most patients are encouraged to walk within a few hours to promote healing.
Monitoring of vitals and oxygen levels
Pain managed with medications
Liquid diet started gradually
Hospital stay is usually 2–3 days
8. Transition to Recovery and Healing
Once stable, the patient begins the recovery phase. This includes dietary progression, gradual physical activity, and follow-up visits. The body slowly adapts to the new digestive system.
Liquid diet followed by soft foods
Gradual return to daily activities
Nutritional supplements are introduced
Long-term lifestyle changes begin
How Gastric Bypass Helps With Weight Loss
Weight loss after gastric bypass happens because of multiple combined effects:
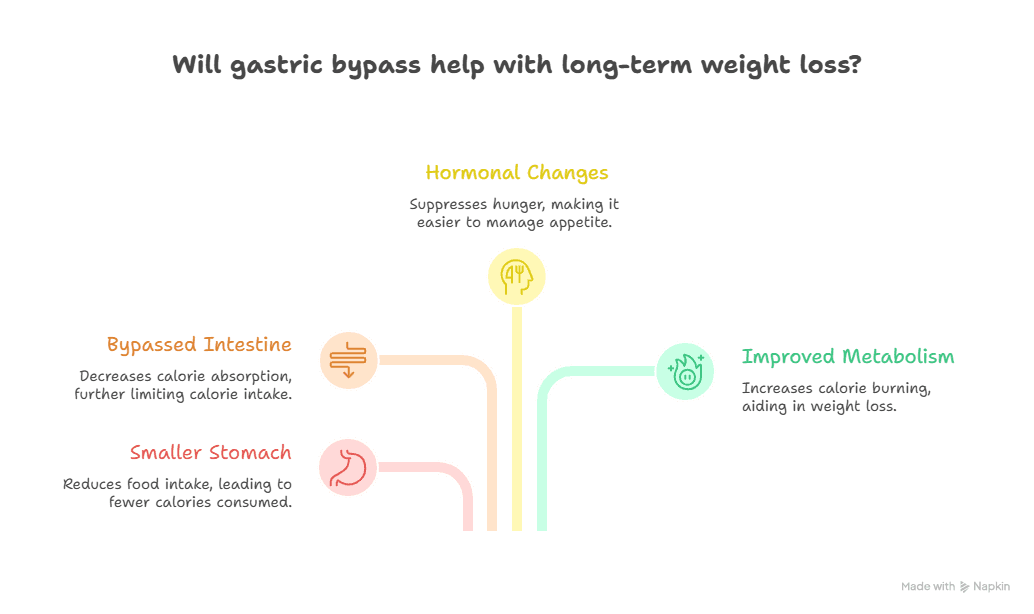
Smaller stomach = less food intake
Bypassed intestine = fewer calories absorbed
Hormonal changes = reduced hunger
Improved metabolism
Most patients lose:
60–75% of excess body weight
Over 12–18 months after surgery
Unlike crash diets, this weight loss is usually long-term when lifestyle changes are followed.
How Gastric Bypass Improves Medical Conditions
Another important part of understanding how does gastric bypass work is knowing how it improves obesity-related diseases.
Conditions That Often Improve or Resolve:
Type 2 diabetes
High blood pressure
High cholesterol
Sleep apnea
Joint pain
Fatty liver disease
In many cases, blood sugar levels improve within days after surgery—sometimes even before major weight loss begins. This makes gastric bypass a powerful metabolic surgery, not just a weight loss tool.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Gastric Bypass?
Gastric bypass is usually recommended for people who:
Have a BMI of 35 or more with medical conditions
Have a BMI of 40 or higher
Have failed to lose weight with non-surgical methods
Are committed to long-term lifestyle changes
A detailed medical evaluation is always done before surgery to ensure safety and suitability.
Is Gastric Bypass Safe?
When performed by an experienced bariatric surgeon, gastric bypass is considered safe and effective.
Modern techniques have:
Reduced complications
Shortened hospital stays
Improved recovery time
Patients are usually encouraged to walk within hours after surgery and resume daily activities gradually.
For patients considering surgery, consulting an experienced specialist like Dr. Aloy Mukherjee helps ensure proper guidance and long-term success.
Long-Term Results of Gastric Bypass
Long-term success depends on:
Following dietary guidelines
Regular physical activity
Medical follow-ups
Mental and emotional support
Most patients maintain significant weight loss even 10–15 years after surgery when lifestyle changes are sustained.
This long-term effectiveness explains why gastric bypass remains a gold-standard bariatric procedure.
Advantages of Gastric Bypass Surgery
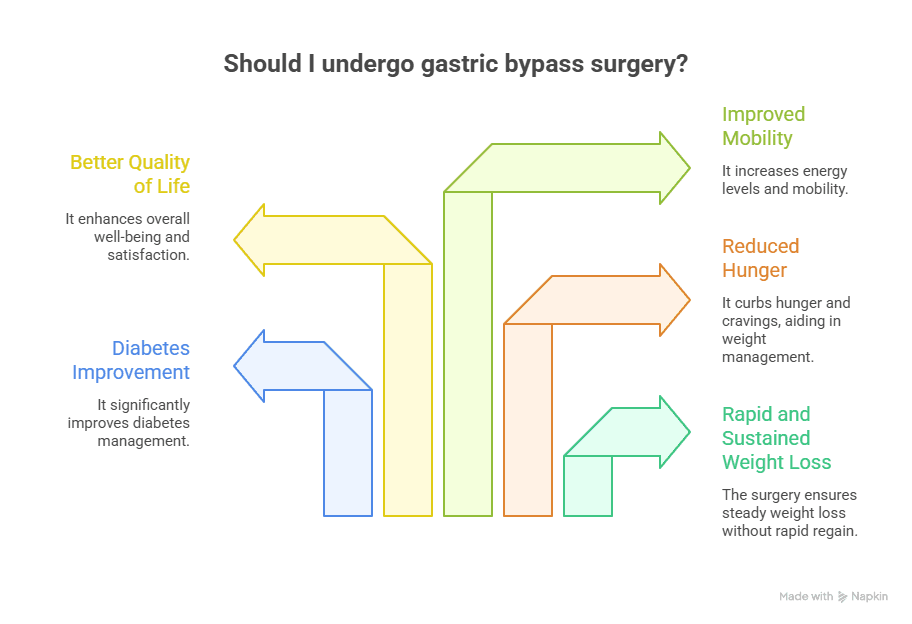
Gastric bypass surgery is known for producing consistent and long-lasting weight loss. By reducing stomach size and limiting calorie absorption, it helps patients lose excess weight steadily rather than rapidly regaining it, which is common with dieting alone.
Rapid and sustained weight loss
Strong improvement in diabetes
Reduced hunger and cravings
Better quality of life
Improved mobility and energy
Final Thoughts
Understanding how does gastric bypass work helps patients make an informed and confident decision about their weight-loss journey. This surgery is not just about eating less; it works by reducing stomach size, limiting calorie absorption, and positively changing hunger-related hormones. Because of this combined effect, gastric bypass supports steady, long-term weight loss and also helps improve serious health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea when lifestyle changes are followed properly.
When performed with proper evaluation, guidance, and long-term follow-up, Gastric Bypass Surgery in Delhi has shown excellent success outcomes for eligible patients. Choosing an experienced bariatric surgeon like Dr. Aloy Mukherjee plays a crucial role in safety, recovery, and sustained results. With commitment to dietary changes, physical activity, and medical care, gastric bypass can be a life-changing step toward better health, improved confidence, and enhanced quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does Gastric Bypass work differently from other weight loss surgeries?
Gastric bypass combines both restriction and reduced absorption, while many other surgeries focus mainly on limiting food intake.
2. How much weight can I lose after gastric bypass?
Most patients lose 60–75% of their excess weight within 12–18 months.
3. How soon does weight loss start after surgery?
Weight loss usually begins immediately and continues steadily over the first year.
4. Does Gastric Bypass cure diabetes?
Many patients experience remission or major improvement in type 2 diabetes shortly after surgery.
5. Will I feel hungry after Gastric Bypass?
Hunger is significantly reduced due to hormonal changes, especially in the first year.
6. Is Gastric Bypass reversible?
Technically it can be reversed, but reversal is rare and only done in special medical situations.
7. How long does it take to recover from Gastric Bypass?
Most patients return to normal daily activities within 2–4 weeks, depending on individual recovery.